Cassava brings life to African people
 Beyond the glittering coastline of what was once known as the Gold Coast, Ghana’s shrublands and rich forested hills are split by forking rivers that reach inland through the country’s lush tropics, into drier western Africa. In the past 40 years, seven major droughts have battered the people of Africa – with the most significant and devastating occurring in the Sahel region and the Horn of Africa in the early 1970s and 1980s.
Beyond the glittering coastline of what was once known as the Gold Coast, Ghana’s shrublands and rich forested hills are split by forking rivers that reach inland through the country’s lush tropics, into drier western Africa. In the past 40 years, seven major droughts have battered the people of Africa – with the most significant and devastating occurring in the Sahel region and the Horn of Africa in the early 1970s and 1980s.
But despite the massive social disruption and human suffering that these droughts cause, life goes on. In south-eastern Ghana and in Togo, the three-million-plus people who speak the Ewe language have a word for this. It is agbeli: ‘There is life’. It is no coincidence that this word is also their name for a tropical and subtropical crop that survives through the worst times to feed Africa’s families: cassava.
Cassava is a lifeline for African people, and is a particularly important staple food for poorer farmers. More cassava is produced in Africa than any other crop, and it is grown by nearly every farming family in sub-Saharan Africa, supplying about a third of the region’s daily energy intake. In the centuries since Portuguese traders introduced this Amazonian plant to Africa, cassava has flourished, yielding up to 40 tonnes per hectare.
Hear more on just why cassava is so important to food security from Emmanuel Okogbenin, of Nigeria’s National Root Crops Research Institute, in the video below (or watch on Youtube):
African countries produced nearly 140 million tonnes of cassava in 2012 – but most of the production is subsistence farming by small-scale farmers. Even the undisputed global cassava giant, Nigeria, currently produces only just enough to feed its population – and although the country is increasingly moving towards production of cassava for export as an industrial raw material, the poorest farmers often do not produce enough to sell, or have access to these markets.
Because cassava does so well on poor soils, on marginal land and with little rainfall, it can outlast its more sophisticated crop competitors: wheat, rice and maize. In fact, under harsh conditions such as drought, the amount of energy a given area of cassava plants can produce in the form of starchy carbohydrates outstrips all other crops. Chiedozie Egesi, a plant breeder and geneticist at Nigeria’s National Root Crops Research Institute (NRCRI), describes cassava as “the crop you can bet on when every other thing is failing”.
Despite cassava’s superhero cape, however, there’s no denying that its production is not at its highest when faced with diseases, pests, low-nutrient soils and drought. How plants deal with problems like low nutrients or dry conditions is called ‘stress tolerance’ by scientists. Improving this tolerance – plus resistance to diseases and pests – is the long-term goal for staple crops around the world so that they have higher yields in the face of capricious weather and evolving threats.
In the 1980s, catastrophe struck cassava production in East and Central Africa. A serious outbreak of cassava mosaic disease (CMD) – which first slowly shrivels and yellows cassava leaves, then its roots – lasted for almost 15 years and nearly halved cassava yields in that time. Food shortages led to localised famines in 1993 and 1997.
Other diseases affecting cassava include cassava brown streak disease (CBSD), cassava bacterial blight, cassava anthracnose disease and root rot. CBSD is impossible to detect above ground. Its damage is revealed only after harvest, when it can be seen that the creeping brown lesions have spoilt the white flesh of the tubers, rendering them inedible. Many cassava diseases are transmitted through infected cuttings, affecting the next generation in the next season. Pests that also prey on cassava include the cassava green mite and the variegated grasshopper.
Between the effects of drought, diseases, pests and low soil nutrients, cassava yields vary widely – losses can total between 50 and 100 percent in the worst times.
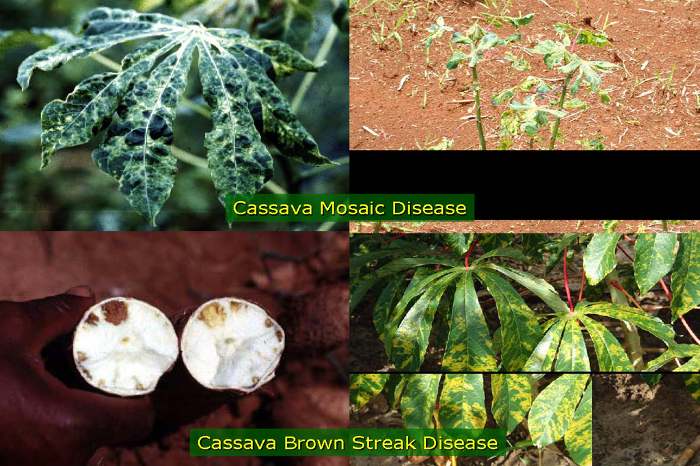

Symptoms of cassava mosaic disease (CMD) and cassava brown streak disease (CBSD), both of which can cripple cassava yields.
GCP takes the first steps to kick start cassava research
The next step forward for cassava appeared to be research towards breeding stronger and more resilient cassava varieties. However, cassava research had long been neglected – scientists say it’s a tricky crop that has garnered far less policy, scientific and monetary interest than the comparatively glamorous crops of maize, rice and wheat.
Watch as Emmanuel tells us more about the complexities and challenges of cassava breeding in the video below (or on YouTube):
Cassava is a plant which ‘drags its feet’: creating new plants has to be done from cuttings, which are costly to cut and handle and don’t store well; the plant takes up to two years to grow to maturity; and it is onerous to harvest. Elizabeth Parkes, of Ghana’s Crops Research Institute (CRI) (currently on secondment at the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture, IITA), says the long wait can be difficult.
This is where the work of scientists funded by the CGIAR Generation Challenge Programme (GCP) came in. Plant breeder and molecular geneticist Emmanuel Okogbenin of NRCRI led the cassava research push launched in 2010. He explains that before GCP, “most national programmes didn’t really have established crop breeding programmes, and didn’t have the manpower” to do the scale of research GCP supported.
Usually, researchers looking to breed crops that are more resistant to drought, diseases and pests would use conventional breeding methods that could take considerable time to deliver any results, especially given cassava’s slow path to maturity. Researchers would be trying to select disease- and pest-resistant plants by looking at how they’re growing in the field, without any way to see the different genetic strengths each plant has.
This is where new ‘molecular breeding’ tools are particularly useful, given that – genetically – cassava presents more of a challenge to breeders than its cereal counterparts. Like many other vegetatively propagated crops, cassava is highly heterozygous, meaning that the counterpart genes on paired chromosomes tend to be different versions, or alleles, rather than the same. This makes it difficult to identify good parent plants for breeding and, after these are crossed, to accurately select progeny with desired traits. Useful – or detrimental – genes can be present in a cassava plant’s genetic code but not reflected in the plant itself, making breeding more unpredictable – and adding extra obstacles to the hunt for the exact genes that code for better varieties of cassava.
Although late to the world of molecular breeding, cassava had not missed its chance. Guided by GCP’s ambitious remit to increase food security through modern crop breeding, GCP-supported scientists have applied and developed molecular breeding methods that shorten the breeding process by identifying which plants have good genes, even before starting on that long cassava growth cycle. Increasing the capacity of local plant breeders to apply these methods has great potential for delivering better varieties to farmers much faster than has traditionally been the case.
Charting cassava’s genetic material was the first step in the researchers’ molecular quest. Part of the challenge for African and South American researchers was to create a genetic map of the cassava genome. Emmanuel describes the strong foundation that these early researchers built for those coming after: “It was significant when the first draft of the cassava genome sequence was released. It enabled rapid progress in cassava research activities and outcomes, both for GCP and cassava researchers worldwide.”
Once cassava’s genome had been mapped, the pace picked up. In just one year, GCP-supported scientists phenotyped and genotyped more than 1000 genetically different cassava plants – that is, measured and collected a large amount of information about both their physical and their genetic traits – searching for ‘superstar’ plants with resistance to more than one crop threat. During this process, scientists compare plant’s physical characteristics with their genetic makeup, looking for correlations that reveal regions of the DNA that seem to contain genes that confer traits they are looking for, such as resistance to a particular disease. Within these, scientists then identify sequences of DNA, or ‘molecular markers’, associated with these valuable genes or genetic regions.
Plant breeders can use this knowledge to apply an approach known as marker-assisted selection, choosing their breeding crosses based directly on which plants contain useful genes, using markers like tags. This makes producing better plant varieties dramatically faster and more efficient. “It narrowed the search at an early stage,” explains Emmanuel, “so we could select only material that displayed markers for the genetic traits we’re looking for. There is no longer any need to ship in tonnes of plant material to Africa.”
Like breadcrumbs leading to a clue, breeders use markers to lead to identifying actual genes (rather than just a site on the genome) that give certain plants desirable characteristics. However, this is a particularly difficult process in cassava. Genes are often obscured, partly due to cassava’s highly heterozygous nature. In trials in Africa, where CMD is widespread, resistant types were hard to spot when challenged with the disease, and reliably resistant parents were hard to pin down.
This meant that two decades of screening cassava varieties from South America – where CMD does not yet exist yet – had identified no CMD-resistance genes. But screening of cassava from Nigeria eventually yielded markers for a CMD-resistance gene – a great success for the international collaborative team led by Martin Fregene, who was based in Colombia at the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT).
This finding was a win for African plant breeders, as it meant they could use molecular breeding to combine the genes producing high-quality and high-yielding cassava from South America with the CMD-resistance gene found in cassava growing in Nigeria.
Chiedozie Egesi, who led the work on biotic trait markers, explains the importance of combining varieties from South America with varieties from Africa: “Because cassava is not native to Africa, those varieties are not as genetically diverse, so we needed to bring genetic diversity from the centre of origin: South America. Coupling resistance genes from African varieties with genes for very high yields from South America was critical.”
Cassava research leaps forward with new varieties to benefit farmers
GCP’s first investment phase into cassava research stimulated a sturdy injection of people, passion, knowledge and funds into the second phase of research. From the genome maps created during the first phase, some of the world’s best geneticists would now apply genomic tools and molecular breeding approaches to increase and accelerate the genetic gains during breeding, combining farmers’ favourite characteristics with strong resistances and tolerances to abiotic and biotic constraints.
In the sprawling, tropical city of Accra on Ghana’s coast, the second phase of the research was officially launched at the end of the wet season in mid-2010. NRCRI’s Emmanuel Okogbenin coordinated product delivery from the projects, but the roles of Principal Investigator for the different projects were shared between another four individuals.
These were breeder and geneticist Chiedozie Egesi (NRCRI, Nigeria), molecular geneticist Morag Ferguson (IITA), genomic scientist Pablo Rabinowicz (University of Maryland, USA) and physiologist and geneticist Alfredo Alves (Brazilian Corporation of Agricultural Research, EMBRAPA). The team shared the vision of enabling farmers to increase cassava production for cash, well beyond subsistence levels.
If the Accra launch set the stage for the next five years of cassava collaboration, a breakthrough in Nigeria at the end of 2010 set the pace, with the release of Africa’s first cassava variety developed using molecular-breeding techniques. “It was both disease-resistant and highly nutritious – a world-first,” recalls Emmanuel proudly.
Known as UMUCASS33 (or CR41-10), it took its high yield and nutritional value from its South American background, and incorporated Nigerian resistance to devastating CMD attacks thanks to marker-assisted selection. It was also resistant to several other pests and diseases. UMUCASS33 was swiftly followed by a stream of similar disease-busting varieties, released and supplied to farmers.
Never before had cassava research been granted such a boost of recognition, scientific might and organisational will. And never before had there been so much farmer consultation or so many on-farm trials.
“Cassava was an orphan crop and with the help of GCP it is becoming more prominent,” says Chiedozie. “GCP highlighted and enhanced cassava’s role as a major and reliable staple that is important to millions of poor Africans.”
Another important challenge for scientists was to develop a higher-yielding cassava for water-limited environments. The aim was to keep mapping genes for resistance to other diseases and pests and then combine them with favourable genetics that increase yield in drought conditions – no easy feat. Drought’s wicked effect on cassava is to limit the bulk of the tuber, or sometimes to stop the tuber forming altogether. Emmanuel led the work on marker-assisted recurrent selection for drought.
Hear from Chiedozie on the beneficial outcomes of GCP – in terms not only of variety releases but also of attracting further projects, prestige, and enthusiastic young breeders – in the video below (or on YouTube):
Many traits and many varieties
As closely as the cassava teams in Africa were working together, Chiedozie recalls that each country’s environment demanded different cassava characteristics: “We had to select for what worked best in each country, then continue with the research from there. What works fine for East Africa may not be so successful in Nigeria or Ghana”. A core reference set representing most of the diversity of cassava in Africa was improved with the addition of over 564 varieties. Improving the reference set, says project leader Morag Ferguson, “enables the capture of many diverse features of cassava” within a relatively small collection, providing a pathway for more efficient trait and gene discovery.
While mapping of cassava’s genetic makeup carried on, with a focus on drought tolerance, researchers continued to develop a suite of new varieties. They mapped out further genes that provided CMD resistance. In Tanzania, four new varieties were released that combined resistance to both CMD and CBSD – two for the coastal belt and two for the semi-arid areas of central Tanzania. These new varieties had the potential to double the yield of existing commercial varieties. In Ghana too, disease-resistant varieties were being developed.
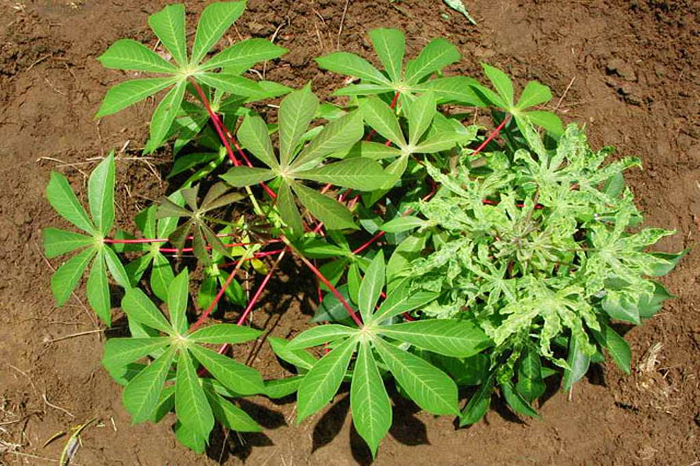

Built-in disease resistance can make a huge difference to the health of cassava crops. This photo shows a cassava variety resistant to African cassava mosaic virus (ACMV), which causes cassava mosaic disease (CMD), growing on the left, alongside a susceptible variety on the right.
Meanwhile in Nigeria, another variety was released in 2012 with very high starch content – an essential factor in good cassava. This is a critical element to breeding any crop, explains Chiedozie: “A variety may be scientifically perfect, based on a researcher’s perspective, but farmers will not grow it if it fails the test in terms of taste, texture, colour or starchiness.”
Geoffrey Mkamilo, cassava research leader at Tanzania’s Agricultural Research Institute, Naliendele, says that farmer awareness and adoption go hand in hand. Once they had the awareness, he says, “the farmers were knocking on our doors for improved varieties. They and NGOs were knocking and calling.”
After groundwork in Ghana and Nigeria to find potential sources of resistance, cassava varieties that are resistant to bacterial blight and green mites were also developed in Tanzania and then tested. By the time GCP closed in December 2014, these varieties were on their way to commercial breeders for farmers to take up.
Scientists seeking to resolve the bigger challenge of drought resistance have achieved significant answers as well. Researchers have been able to map genetic regions that largely account for how well the crops deal with drought.
Hunt for ‘super powered’ cassava
The hunt was on for drought-tolerance genes in African cassava plants. The end goal was to find as many different drought-related genes as possible, then to put them all together with the applicable disease and pest resistance genes, to make a ‘super powered’ set of cassava lines. Molecular breeders call this process ‘pyramiding’, and in Ghana, Elizabeth Parkes led these projects.
With the help of Cornell University scientists, the researchers compared plants according to their starch content, how they endured a dry season, how they used sunlight and how they dealt with pests and diseases.
Fourteen gene regions or quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were identified for 10 favourable traits from the genetic material in Ghana, while nine were found for the plants in Nigeria – with two shared between the plants from both Ghana and Nigeria. After that success, the identified genes were used in breeding programmes to develop a new generation of cassava with improved productivity.
Pyramiding is important in effective disease resistance; Chiedozie explains in the video below (or on YouTube):
The research has also delivered results in terms of Vitamin A levels in cassava. In 2011, the NRCRI team, together with IITA and HarvestPlus (another CGIAR Challenge Programme focussed on the nutritional enrichment of crops), released three cassava varieties rich in pro-vitamin A, which hold the potential to provide children under five and women of reproductive age with up to 25 percent of their daily vitamin A requirement. Since then, the team has aimed to increase this figure to 50 percent. In 2014, they released three more pro-vitamin A varieties with even higher concentrations of beta-carotene.
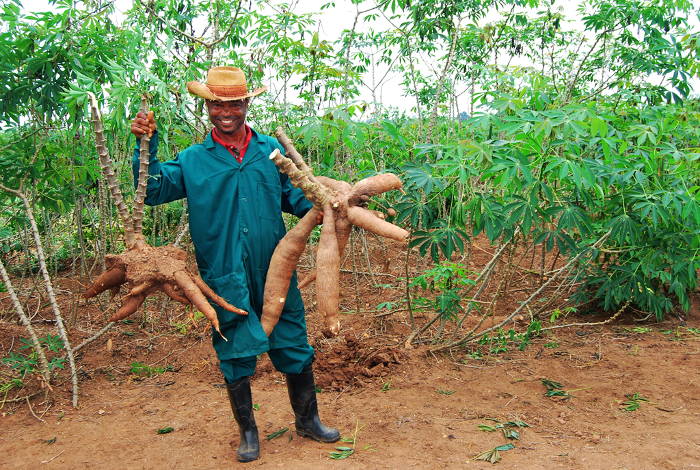

A field worker at IITA proudly displays a high-yielding, pro-vitamin A-rich cassava variety (right), compared with a traditional variety (left).
The new varieties developed with GCP support are worth their weight in gold, says Chiedozie: “Through these varieties, people’s livelihoods can be improved. The food people grow should be nutritious, resistant and high-yielding enough to allow them to sell some of it and make money for other things in life, such as building a house, getting a motorbike or sending their kids to school.”
Turning from Nigeria to Tanzania, Geoffrey has some remarkable numbers. He says that the national average cassava yield is 10.5 tonnes per hectare. He adds that a new cassava variety, PWANI, developed with GCP support and released in 2012, has the potential to increase yields to 51 tonnes per hectare. And they don’t stop there: the Tanzanian researchers want to produce three million cuttings and directly reach over 2,000 farmers with these new varieties, then scale up further.
Cassava grows up: looking ahead to supporting African families
Emmanuel reflects on how the first release of a new disease-resistant high-yielding cassava variety took fundamental science towards tangible realities for the world’s farmers: “It was a great example of a practical application of marker technology for selecting important new traits, and it bodes well for the future as markers get fully integrated into cassava breeding.”
Emmanuel further believes that GCP’s Cassava Research Initiative has given research communities “a framework for international support from other investors to do research and development in modern breeding using genomic resources.” Evaluations have demonstrated that molecular-assisted breeding can slash between three and five years from the timeline of developing better crops.

Women tend to bear most of the burden of cassava cultivation and preparation. Here a Congolese woman pounds cassava leaves – eaten in many regions in addition to cassava roots – prior to cooking a meal for her family.
But, like cassava’s long growth cycle underground, Emmanuel knows there is still a long road to maturity for cassava as a crop for Africa and in research. “Breeding is just playing with genetics, but when you’re done with that, there is still a lot to do in economics and agronomics,” he says. Revolutionising cassava is about releasing improved varieties carefully buttressed by financial incentives and marketing opportunities.
Rural women in particular stand to benefit from improved varieties – they carry most of the responsibility for producing, processing and marketing cassava. So far, Elizabeth explains: “Most women reported an increase in their household income as a result of the improved cassava, but that is still dependent on extra time spent on cassava-related tasks” – a burden which she aims to diminish.
Elizabeth emphasises that future improvement research has to take a bottom-up approach, first talking to female farmers to ensure that improved crops retain characteristics they already value in addition to the new traits. “Rural families are held together by women, so if you are able to change their lot, you can make a real mark,” she says. Morag echoes this hope: “We are just starting to implement this now in Uganda; it’s a more farmer-centric approach to breeding”. The cassava teams emphasise the importance of supporting women in science too; the Tanzanians teams are aiming for a target of 40 percent women in their training courses.
Meet Elizabeth in the podcast below (or on PodOmatic), and be inspired by her passion when it comed to women in agriculture and in science:
This direct impact goes much further than individuals, says Chiedozie. “GCP’s daring has enabled many national programmes to be self-empowered, where new avenues are unfolding for enhanced collaboration at the local, national and regional level. We’re seeing a paradigm shift.” And Chiedozie’s objectives reach in a circle back to his compatriots: “Through GCP, I’ve been able to achieve my aims of using the tools of science and technology to make the lives of poor Africans better by providing them with improved crops.”
GCP has been crucial for developing the capacity of countries to keep doing this level of research, says Chiedozie: “The developing-country programmes were never taken seriously,” he says. “But when the GCP opportunity to change this came up we seized it, and now the developing-country programmes have the boldness, capacity and visibility to do this for themselves.”
Emmanuel says his proudest moment was when GCP was looking for Africans to take up leadership roles. “They felt we could change things around and set a precedent to bring people back to the continent,” he says. “They appreciated our values and the need to install African leaders on the ground in Africa rather than in Europe, Asia or the Americas.”
“If you want to work for the people, you have to walk with the people – that’s an African concept. Then when you work with the people, you really understand what they want. When you speak, they know they can trust you.” GCP trusted and trod where others had not before, Chiedozie says.
Elizabeth agrees: “In the past, the assumption was always that ‘Africa can’t do this.’ Now, people see that when given a chance to get around circumstances – as GCP has done for us through the provision of resources, motivation, encouragement and training – Africa can achieve so much!”
More links
- Profiles here on the Sunset Blog: Elizabeth’s story | Chiedozie’s story
- And an extra Sunset helping of cassava in the stories of our partnerships: ARI, Tanzania | CRI, Ghana | NRCRI, Nigeria
- Cassava blogposts on the GCP Blog
- Cassava presentations (on SlideShare)
- Cassava video playlist from Chiedozie and Emmanuel (on YouTube)
- Cassava podcasts from Elizabeth (on PodOMatic)
- Cassava Community of Practice (on IBP website)
- Cassava Research Initiative | InfoCentre